Bottle Tree (Chorisia speciosa)
Click on the photo to zoom
![]() For more information contact us at 26510 22282
For more information contact us at 26510 22282
Product description
Ceiba (Chorisia) speciosa
Family: Malvaceae
Description
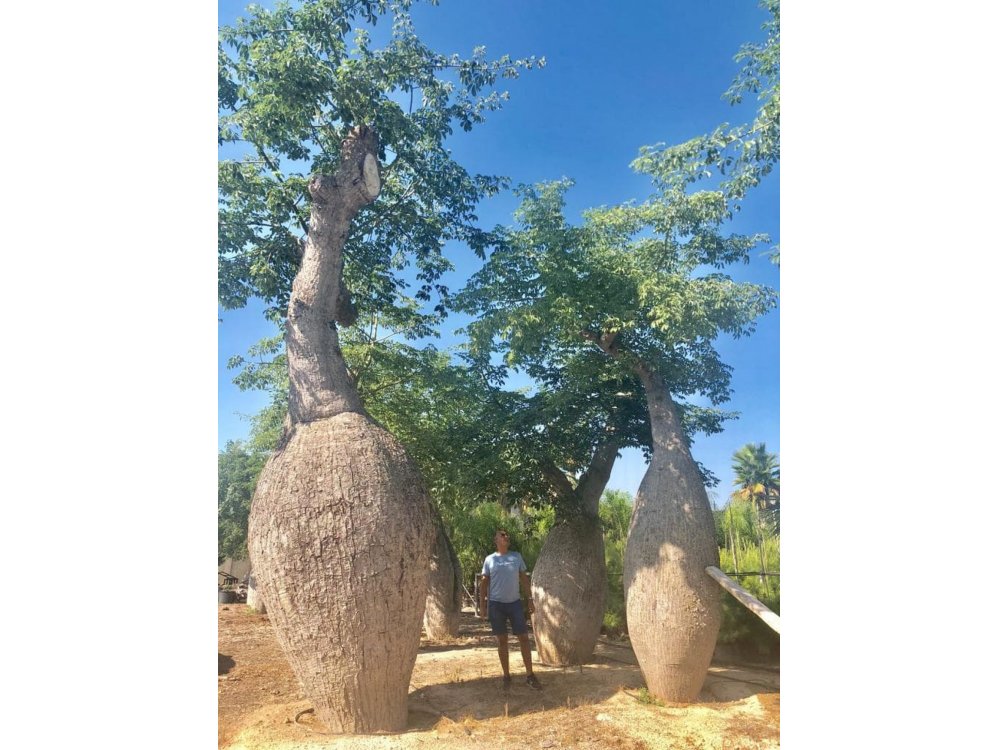
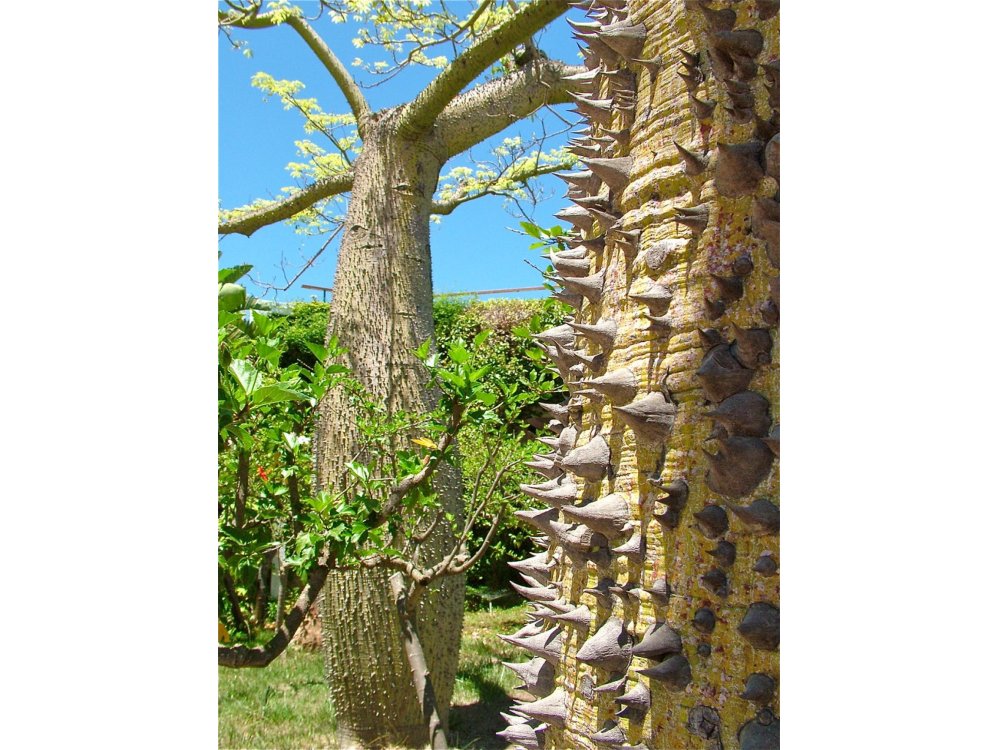
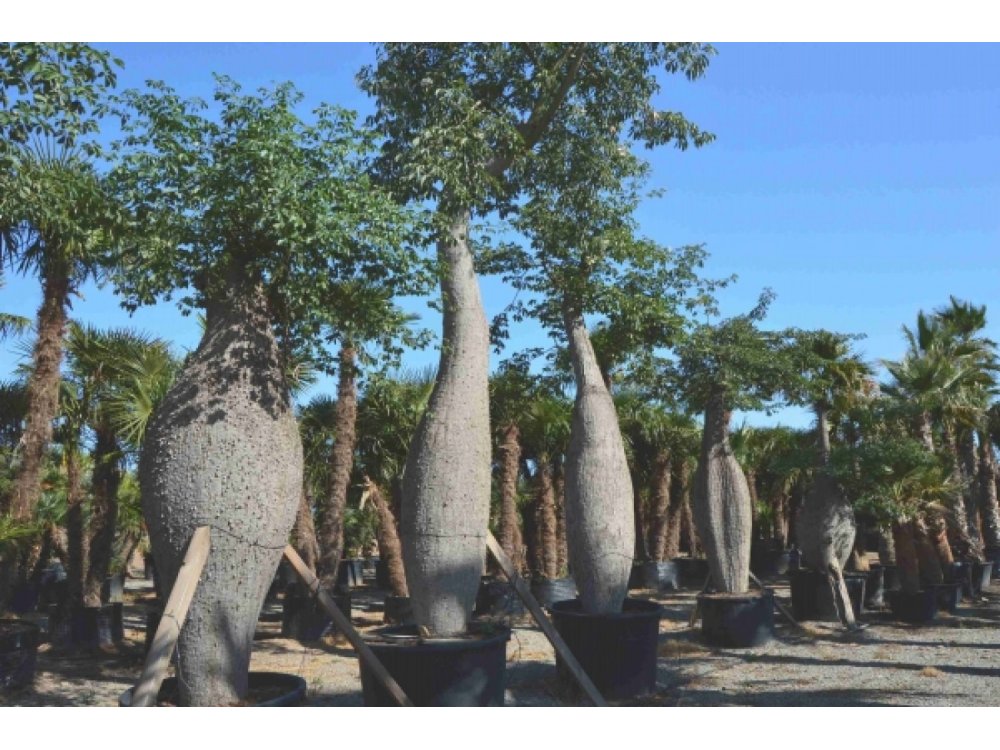
Native deciduous tree in the tropical and subtropical forests of South America that is found under the common name silk floss tree and with the synonym Chorisia speciosa. It grows rapidly when water is abundant, and sometimes reaches over 25m in height. But it usually reaches 12-18m high and 6-12m wide. Its trunk is bottle-shaped and full of thick, sharp, conical spines that prevent wild animals from climbing trees. In younger trees, the trunk is green because of its high chlorophyll content, which makes it capable of carrying out photosynthesis when leaves are absent. With age it turns gray. The branches tend to be horizontal and are also covered with thorns. The leaves consist of 5 to 7 long leaflets. The flowers are creamy-white in the center and pink towards the ends of their five petals and have a diameter of 10-15cm. Their nectar is known to attract insects and hummingbirds. The flowers appear from February to May, but can also bloom at other times of the year. As a deciduous tree, it is completely bare of leaves and flowers during the winter months. The fruits are oval-shaped capsules 20cm long containing black bean-sized seeds surrounded by a mass of fibrous, fluffy material resembling cotton or silk.
Cultivation
Prefers sunny positions and well-drained soils. It is resistant to drought and moderate cold. Blooms best when watered regularly most of the time, but kept a little dry in late summer. It drops its leaves when the temperature drops below -2.7ºC, but established trees have been known to survive frosts below -6.5ºC. Young trees need protection from frost. Propagation can be achieved by rooting semi-ripe cuttings of the top taken during a period of rapid shoot growth in a closed container with heat from below.
Uses
It is mainly grown for ornamental purposes. In addition to private gardens around the world, they are often planted along city streets.Also, the tree's wood can be used to build canoes and to create paper. The bark has been used to make ropes. In addition, vegetable oil (both edible and industrially useful) can be obtained from the seeds.















 Forest Fruit Plants
Forest Fruit Plants Spice Herbs Medicinal seeds
Spice Herbs Medicinal seeds Bulbs
Bulbs Fruit Trees
Fruit Trees Garden Materials
Garden Materials Ornamental Plants
Ornamental Plants Grapevine Plants
Grapevine Plants Onion Set
Onion Set Fertilizers
Fertilizers Potato seed
Potato seed Seeds
Seeds Roses
Roses Tropical Plants
Tropical Plants Home Pesticides
Home Pesticides














